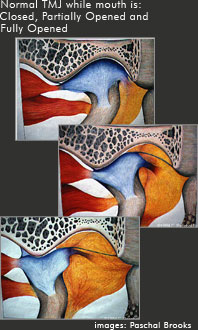
Each person has two TMJ joints that are used to open and close our mouths when we chew, talk, and swallow.
The TMJ connects the lower jaw (mandible) to the skull. The lower jaw and the skull are connected by a number of muscles and ligaments, which function in harmony when the lower jaw is in the correct position. The head of the lower jaw bone is called a condyle and it fits into the concavity of the temporal bone called the glenoid fossa and are separated by an articular disc. The two bones of the TMJ are held together by a series of ligaments.
For normal function to occur, a piece of cartilage called an articular disc acts as a cushion or shock absorber between the two bones. Since the disc is attached by muscle, it actually moves with the movement of the TMJ. When the lower jaw opens and closes, the disc stays between the condyle and the glenoid fossa of the temporal bone at all times.
If you notice discomfort or pain have your jaw joint checked by a dentist who treats patients with jaw joint disorders!
For more on TMJ Health and Treatments visit the Toronto TMJ Centre's website here.